In disability studies, there are ongoing debates about the best ways to learn more about the experience and consequences of disability. At present, emancipatory research appears to be a favoured approach, yet it has many critics. It is grounded in principles such as: a focus on removing barriers, consumer-research collaborations during all stages of research, and an emphasis on the priorities of the disability community.
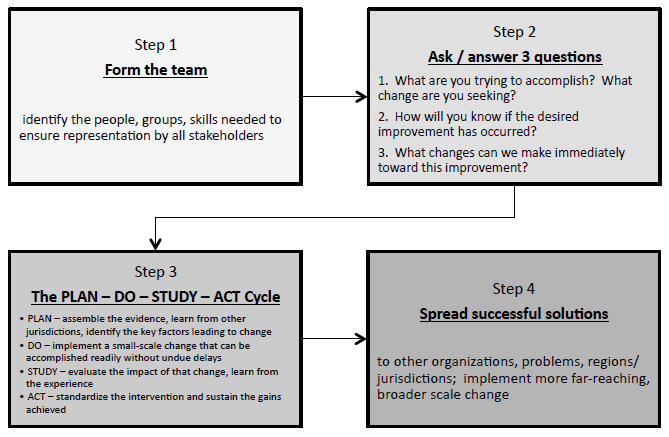
One way of conducting emancipatory research is the Learning Collaborative. This approach is designed to accelerate change and remove barriers by engaging stakeholders; identifying the goal and improvement measures; implementing “plan, do, study, act” cycles; and sharing successful solutions with others.
The Learning Collaborative methodology is composed of brief research cycles made up of 4 steps. We have adapted the Plan-Do Study-Act (PDSA) model of other policy improvement models to include the following:
Plan
Choose one small manageable area that affects the lives of people with disabilities that can be traced back to the policy environment. The best issues are the ones that policy makers have a mutual interest in addressing. Identify stakeholders, assemble evidence, conduct policy analysis, compare jurisdictions, identify best practices, review literature.
Do
Gather and disseminate research findings to policy makers that would shed light on the issue and make recommendations for best practices.
Study
Study the effectiveness of the knowledge mobilization initiative, and gather new information from knowledge users on how this could be done more effectively.
Act
Incorporate this learning into future knowledge mobilization to a broader group of stakeholders. Refine knowledge mobilization instruments and approaches.
The learning collaborative methodology is used along with the Disability policy lens in all CDPA research.
A paper called, “The Learning Collaborative: An approach to emancipatory research in disability studies” describes how the the Learning Collaborative approach was used to improve accessibility in primary care settings. In addition to embracing many of the emancipatory research principles, it adds a level of rigour through the use of evidence-based policy analysis and scoping review methodology.
To view the article click below.
The Learning Collaborative: An approach to emancipatory research in disability studies
To visit the Canadian Journal of Disability Studies click below.